Digital advertising is going through one of its biggest shifts ever. With browsers phasing out third-party cookies and privacy rules getting stricter, marketers can no longer rely on tracking people across the internet the way they used to. As a result, brands are rethinking how they reach the right audience, without invading user privacy.
This is where contextual targeting is making a strong comeback.
Instead of following users around based on their past behavior, contextual targeting places ads based on the content people are viewing in the moment. It matches ads with relevant articles, videos, keywords, and topics, making it both privacy-friendly and highly effective.
The best part?
You still get strong engagement and better relevance without needing any personal data.
In this blog, we’ll discuss how contextual targeting works, why it’s becoming essential in a cookieless world, and how brands can use it to drive results.
Jump ahead to:
What Is Contextual Targeting?
Contextual targeting (also known as contextual advertising) refers to placing ads based on the content and context of the webpage-rather than relying on a user’s personal data or browsing history. The system analyses what the page is about (its topics, themes, keywords, etc.) and delivers ads that match that context.
In other words: if a user is reading about cooking recipes or travel tips, contextual targeting ensures ads related to cooking equipment, cookware, travel deals, or holiday accessories show up – because those ads align with what the user is currently reading.
How It Differs from Behavioral Targeting
- Basis of targeting
- Contextual targeting depends ONLY on the content of the page (what the user is reading or viewing right now).
- Behavioral targeting, on the other hand, uses a user’s past online behavior – browsing history, searches, clicks, purchases – to serve ads believed relevant to that user.
- Contextual targeting depends ONLY on the content of the page (what the user is reading or viewing right now).
- Personalization vs. Context-sensitivity
- Behavioral targeting delivers personalized ads tailored to individual preferences or inferred interests.
- Contextual targeting emphasizes context – what the user is seeing now – not who the user is. So it’s not personalized per se, but relevant to the moment.
- Behavioral targeting delivers personalized ads tailored to individual preferences or inferred interests.
- Privacy and data reliance
- Behavioral targeting typically relies on cookies or other identifiers (user data), which raises privacy and regulatory concerns.
- Contextual targeting does not need to collect or store individual user data, making it more privacy-friendly – especially in a cookieless or privacy-conscious world.
- Behavioral targeting typically relies on cookies or other identifiers (user data), which raises privacy and regulatory concerns.
- Relevance in real time
- Contextual works “in the moment,” aligning with what the user is consuming now.
- Behavioral looks at past behavior and makes predictions about what user might like – but this may not always match their present mindset or interest.
- Contextual works “in the moment,” aligning with what the user is consuming now.
Why Contextual Targeting Matters in a Cookieless World
As third-party cookies disappear and privacy rules tighten, contextual targeting has become one of the safest and most reliable ways for advertisers to reach audiences without tracking them.
1. Privacy Regulations (GDPR, CCPA)
Laws like GDPR and CCPA limit how companies collect, store, and use personal data. This makes traditional behavioral targeting harder and riskier.
Contextual targeting solves this by not using any personal data at all – ads are matched purely to page content.
2. Browser Restrictions
Safari and Firefox already block third-party cookies by default. Chrome – which controls over half of global browser share – is also phasing them out. As a result, advertisers need methods that don’t rely on cookies to keep campaigns performing. Contextual targeting works seamlessly even when cookies are blocked.
3. Rising User Distrust Around Data Tracking
People are increasingly uncomfortable with being tracked across sites. Studies show users prefer ads that don’t rely on personal or behavioral data.
Contextual targeting aligns with what users want: relevant ads without surveillance.
4. Benefits: Privacy-Friendly, Future-Proof, and Scalable
Because contextual targeting doesn’t use personal identifiers, it stays fully compliant with global privacy laws and browser changes. Marketers get:
- High relevance because ads match the content users are consuming
- Brand safety through content-based filtering
- Scalability across channels and websites
- Future-proof performance since it works even when cookies disappear
Also Read: First Party Data: The Answer to Third Party Cookie Loss
How Contextual Targeting Works
1. Content Analysis
- The ad-tech system scans the content of a web page: text, metadata, sometimes images – to understand what the page is about.
- It extracts relevant keywords, topics, themes, and sometimes sentiment or tone – basically “what is this page about?”
2. Semantic Understanding
Rather than just matching exact keywords, modern contextual-targeting tools use Natural Language Processing (NLP) and sometimes machine-learning / AI algorithms to understand the meaning and context of the page. This helps them interpret even subtle references, synonyms, or tone – not just literal words.
- This semantic targeting ensures ads are relevant even if the page doesn’t contain exact keywords – for example, an article about “urban mobility challenges” could be matched with ads for e-bikes, even without the term “electric bike.”
3. Real-Time Page Classification & Matching
- Once the content is analyzed and classified (topic, category, language, tone), this information gets passed to ad-serving platforms (SSPs / DSPs / ad exchanges) in real time, often as part of the bid request.
- Based on those contextual signals, the ad platform picks (or bids for) ads whose targeting criteria match that content context – rather than user data.
4. Ad Delivery Based on Context – Not User Identity
- The ad that best matches the context (topic, keywords, sentiment, page quality) gets displayed – regardless of who the user is or their browsing history.
- This makes the process privacy-friendly (no user tracking), while still delivering relevant ads because they match what the user is reading or viewing now.
Also Read: Demise of Third Party Cookies and Its Impact on Marketing
Types of Contextual Targeting
Contextual targeting can take different forms depending on how advertisers want to match their ads with content. Here are the main types:
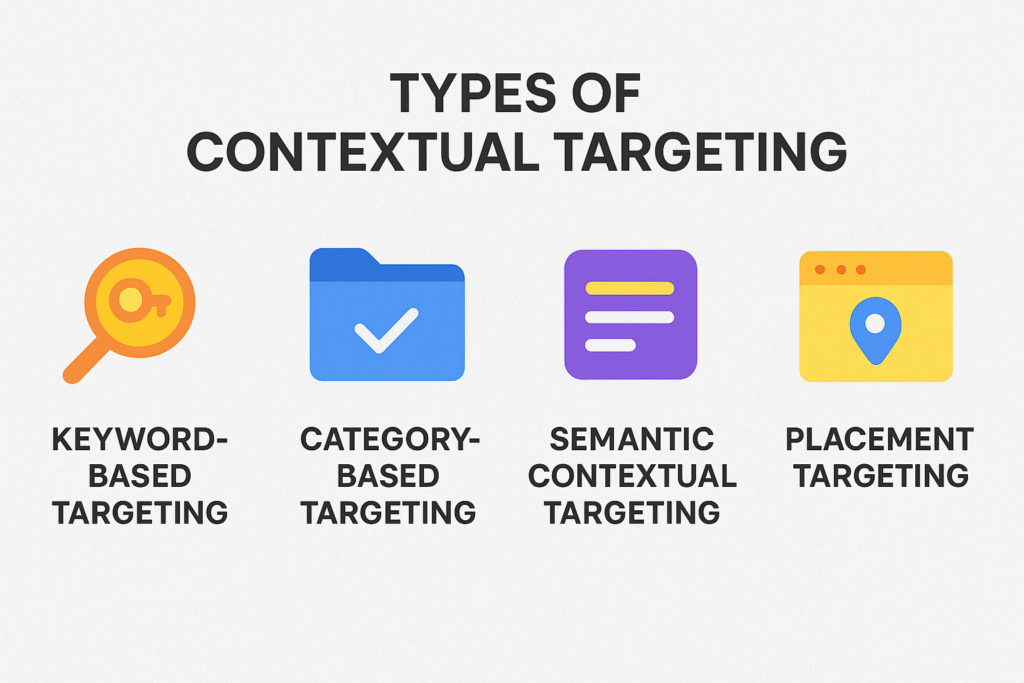
1. Keyword-Based Targeting
- This is the most basic form: the ad system looks for specific keywords or phrases on a webpage. If the page content includes those keywords, an ad may be placed there.
- Example: A travel company targeting the keyword “summer vacation” – its ad may show up on a blog post discussing summer travel plans.
- This gives advertisers direct control over what kind of content triggers their ads.
2. Category-Based Targeting
- Instead of looking for individual keywords, this method targets predefined content categories or verticals – e.g. “Health & Fitness,” “Technology,” “Travel,” “Finance,” etc.
- Ads are placed on any webpages classified under those categories, even if exact keywords aren’t present.
- Example: A fitness gear brand can choose the “Sports & Fitness” category – their ads may appear across various fitness-related posts (workout tips, healthy eating, gym reviews, etc.), regardless of the specific terms used.
3. Semantic (AI-Driven) Contextual Targeting
- This is a more advanced form where systems use AI, machine learning, or Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand the meaning, themes, and context of a page – not just match keywords.
- The system can interpret semantics, avoid false matches (e.g. differentiate “Apple” the fruit vs. “Apple” the company), and ensure ad relevance even if keywords are ambiguous or not present.
- This helps reduce mismatches and improve targeting accuracy and brand safety.
4. Placement Targeting (Specific URLs or Sites)
- Sometimes advertisers want to place ads on particular websites or known high-value publications – regardless of specific keywords or categories. This is called placement targeting (or “site-specific contextual targeting”).
- It allows advertisers to hand-pick where their ads appear – useful if certain websites align strongly with brand image or the target audience.
Quick Comparison
| Targeting Type | What it Matches On | Best Use Case / Strength |
| Keyword-based | Specific words/phrases in content | High control, narrow targeting for niche products |
| Category-based | Broad content categories/topics | Reach a wider audience in a relevant vertical |
| Semantic (AI-driven) | Meaning, context, themes (beyond words) | More accurate, context-aware, and reduces mismatch risk |
| Placement targeting | Specific websites/pages | Target known high-value or brand-safe sites directly |
Benefits of Contextual Targeting
1. Reaches High-Intent Users Without Tracking Them
Contextual targeting places ads where the user’s current content matches your offering – meaning you catch people when they’re already showing interest.
For example, an online education platform can reach students seeking exam or assignment help – without using personal data.
2. Improves Brand Safety
Because ads appear only on pages that match approved topics, categories, or sentiment, advertisers avoid risky or inappropriate placements.
Contextual tools can filter out negative, controversial, or unsafe content.
3. Higher Relevance = Better Engagement
When ads align with what users are reading, they feel more natural and helpful – boosting clicks, time on site, and conversions.
4. Scalable Across Channels
Contextual targeting works across websites, mobile apps, CTV, YouTube, and even audio – making it easy to scale campaigns across formats.
5. Works Even With Privacy Changes / Blocked IDs
No cookies, no device IDs, no personal data needed.
This makes contextual targeting future-proof in a world where:
- Safari & Firefox block cookies
- Chrome is phasing them out
- GDPR/CCPA limit data tracking
Contextual Targeting vs. Behavioral Targeting
As third-party cookies fade out, marketers often compare two major approaches: contextual and behavioral targeting. Here’s how they differ across the key dimensions:
| Aspect | Contextual Targeting | Behavioral Targeting |
| Data Needed | Page content only | User behavior/history |
| Privacy | Very high | Low–moderate |
| Reach | Broad (non-dependent on cookies) | Shrinking |
| Accuracy | High in-the-moment intent | Based on past actions |
| Performance | Consistent, often cheaper | Strong but declining |
| Future-Proof | Yes | No |
How Advertisers Can Implement Contextual Targeting
1. Define campaign goals
Start with the outcome you want: brand awareness, lead gen, product sales, store visits, or app installs. Goals shape which contexts and KPIs matter (CTR, viewability, view-through conversions).
2. List relevant contexts & topics
Make a short list of page themes where your audience is likely to be receptive (e.g., “running & fitness,” “plant-based cooking,” “personal finance for millennials”). Think about intent – why someone reading that content would care about your product.
3. Create keyword clusters
Group keywords around each context (primary + related/long-tail). Example for fitness: “running shoes,” “marathon training,” “best trail sneakers,” “post-run recovery.” Use these clusters to guide keyword-based or semantic targeting.
4. Use contextual segments from ad platforms
Leverage ready-made contextual segments on DSPs/SSPs (topics, categories, sentiment). These save time and scale faster than hand-curated lists. Combine platform segments with your keyword clusters for tighter targeting.
5. Apply brand safety & suitability filters
Add negative categories (e.g., hate speech, adult, illegal content) and fine-tune suitability (exclude extreme political content, sensationalism). Test both broad and strict safety settings to balance reach and protection.
Challenges & Limitations of Contextual Targeting
| Challenge | What It Means |
| Harder to Personalize | Ads are based on page content, not user identity – making personalization limited. |
| Less Granular Than Behavioral Targeting | You can’t target niche segments like “cart abandoners” or “recent purchasers.” |
| Keyword Over-Reliance | Basic keyword targeting can cause mismatches or missed opportunities if the context is misunderstood. |
| Risk of Context Mismatch | Poor setup may place ads next to irrelevant, low-quality, or negative-sentiment content. |
| Measurement Complexity | Without user tracking, attribution becomes harder; depends on contextual performance, not user paths. |
How EasyInsights Enhances Contextual Targeting
When you use contextual targeting, ad relevance and brand safety are important – but so is reliable measurement, attribution and clean data. EasyInsights helps bridge that gap, making contextual advertising more effective, measurable and future-ready. What EasyInsights Adds to Contextual Campaigns:
- Cross‑Channel Attribution & Conversion Tracking
EasyInsights uses server‑side tracking (its “pixel”) to collect first‑party data across web, mobile, CRM, and even offline channels. This gives a complete view of the customer journey – from first touch to purchase – even when third‑party cookies fail. - Identifies High‑Performing Contexts, Pages & Placements
With consolidated data, EasyInsights enables you to see which content contexts, websites, or pages are delivering better results – helping you optimize by scaling the good placements and dropping underperformers. - Allows Smarter Spend Optimization & Better ROAS
With clear attribution and better data hygiene, marketers can allocate budget where it actually performs. EasyInsights supports custom attribution models (first‑click, last‑click, non-direct, etc.), letting you optimize campaigns, reduce wastage, and improve ROAS.
Conclusion
Contextual targeting has proven to be a scalable, privacy-first, and highly effective way for advertisers to reach relevant audiences without relying on third-party cookies or personal tracking data. By aligning ads with the content users are actively engaging with, brands can drive meaningful engagement, improve ad relevance, and maintain strong brand safety – all while respecting user privacy.
As the digital advertising landscape continues to shift toward stricter privacy regulations and cookieless tracking, now is the time for marketers to future-proof their campaigns. Leveraging tools like EasyInsights can further enhance contextual campaigns, providing accurate cross-channel attribution, clean first-party data, and AI-driven insights to optimize ad spend and maximize ROAS.
Ready to improve your contextual targeting? Book a demo with EasyInsights today.